Cannabinoids. We all know THC (the most famous Cannabinoid) is what most people think about whenever the subject of cannabis is mentioned.
But there are other Cannabinoids which can be used alone or in combinations for all kinds of medical purposes. And, three classes of cannabinoids, CBG, CBC and CBD do not have any psychoactive effect at all.
Confused? This Will Help
 In the most basic sense, cannabinoids are the chemical compounds in weed which match up with the chemical compounds in your body and cause weed to affect you. Cannabinoids are the reason you get high when you smoke weed and they’re also the reason weed can help to heal certain illnesses and afflictions.
In the most basic sense, cannabinoids are the chemical compounds in weed which match up with the chemical compounds in your body and cause weed to affect you. Cannabinoids are the reason you get high when you smoke weed and they’re also the reason weed can help to heal certain illnesses and afflictions.
There are at least 113 cannabinoids found in weed and they all have a slightly different effect. Certain cannabinoids, like THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol), have a psychoactive effect, which is what makes you feel high. Other cannabinoids, like CBD, have more of a somatic effect, affecting the physical functions of your body.
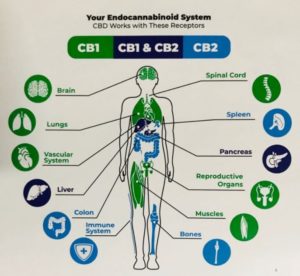
Our bodies contain many receptors. The chief among these are named CB1 and CB2 and were discovered in the mid 1990’s. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain, but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor lives in the immune system and in cells which have to do with the formation of new blood cells.
How Do Cannabinoids Work?
Cannabinoids occur naturally in weed in the form of phytocannabinoids. They also occur naturally in the human body in the form of endocannabinoids. The ones found in the human body are produced in something called the endocannabinoid system, which is responsible for functions like sleep, movement, appetite and emotion.
Brain functions controlled by CB1-modulated neurotransmitters are diverse and of utmost significance as they include how we think, remember, learn new things, express emotions. They also affect bodily movement, fear, stress, pain, appetite and body temperature, among other critical functions.
CB2, is mainly found in the immune system. Once the cannabanoids enter your body, they attach to these receptors, activating the endocannabinoid system and affecting it in different ways depending on the particular cannabinoid.
How Many Cannabinoids Are There?
There are close to 150 other cannabinoids in each and every cannabis plant, most of them still mysterious and full of potential.
Here are some of the Cannabinoids which have been identified to date:
- Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid (THCA)
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Cannabidolic Acid (CBDA)
- Cannabidiol (CBD)
- Cannabinol (CBN)
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
How Much Cannabinoid Research is Occurring?
“New” cannabinoids—chemical compounds that mimic compounds found in the human endocannabinoid system—like CBG (cannabigerol), CBN (cannabinol) and THCP (tetrahydrocannabiphorol) aren’t really new. Heck, they’ve been important cogs in the marijuana machine from first sprout. Until recently, though, they’ve remained under the radar of the mainstream.
There are reasons why very few of cannabis’ almost 150 phytocannabinoids have been isolated and comprehensively studied. Because marijuana is still deemed illegal on a federal level in the U.S., research–and securing funding for that research–can be a tricky endeavor. And because most varieties of cannabis are CBD- or THC-dominant, the isolation and study of “minor” cannabinoids can be challenging.
Cannabinoids, Now What?
Check out these other Blog Post which discuss the chemistry of Cannabis: Terpenes, What the Heck are Terpenes? Trichomes, What the Heck are Trichomes? and Flavinoids, What the Heck are Flavinoids.?
Book a Happy Travelers Tour Cannabis Experience and get up-close-and-personal with Cannabis Plants!