CBD vrs THC
As the legal use of marijuana and other cannabis products grows, consumers are becoming more curious about their options. This includes cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), two natural compounds found in plants of the Cannabis genus.
CBD can be extracted from hemp or from marijuana. Hemp plants are cannabis plants that contain less than 0.3 percent THC, while marijuana plants are cannabis plants that contain higher concentrations of THC. CBD is sold in the form of gels, gummies, oils, supplements, extracts, and more.
THC is the main psychoactive compound in marijuana that gives the high sensation. It can be consumed by smoking marijuana. It’s also available in oils, edibles, tinctures, capsules, and more.
Both compounds interact with your body’s endocannabinoid system, but they have very different effects.
Read on to learn more about these compounds. While they may have a lot in common, they have some key differences that determine how they’re used.
CBD vs. THC: Chemical structure
Both CBD and THC have the exact same molecular structure: 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. A slight difference in how the atoms are arranged accounts for the differing effects on your body.
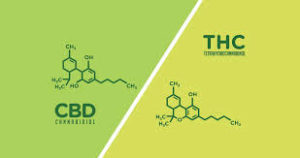 Both CBD and THC are chemically similar to your body’s own endocannabinoids. This allows them to interact with your cannabinoid receptors.
Both CBD and THC are chemically similar to your body’s own endocannabinoids. This allows them to interact with your cannabinoid receptors.
The interaction affects the release of neurotransmitters in your brain. Neurotransmitters are chemicals responsible for relaying messages between cells and have roles in pain, immune function, stress, sleep, to name a few.
CBD vs. THC: Psychoactive components
Despite their similar chemical structures, CBD and THC don’t have the same psychoactive effects. In fact, CBD is a nonpsychoactive compound. That means it doesn’t produce the “high” associated with THC.
THC binds with the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors in the brain. It produces a high or sense of euphoria.
CBD binds very weakly, if at all, to CB1 receptors. In fact, it can interfere with the binding of THC and dampen the psychoactive effects.
CBD vs. THC: Medical benefits
CBD and THC have many of the same medical benefits. They can provide relief from several of the same conditions. However, CBD doesn’t cause the euphoric effects that occur with THC. Some people may prefer to use CBD because of the lack of this side effect.
In June 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approvedTrusted Source Epidiolex, the first prescription medication to contain CBD. It’s used to treat rare, difficult-to-control forms of epilepsy.
CBD is used to help with other various conditions, such as:
- seizures
- inflammation
- pain
- psychosis or mental disorders
- inflammatory bowel disease
- nausea
- migraines
- depression
- anxiety
THC is used to help with conditions such as:
- pain
- muscle spasticity
- glaucoma
- insomnia
- low appetite
- nausea
- anxiety
CBD vs. THC: Side effects
CBD is well-tolerated, even in large doses. ResearchTrusted Source suggests any side effects that occur with CBD use are likely the result of drug-to-drug interactions between CBD and other medications you may be taking.
THC causes temporary side effects, such as:
- increased heart rate
- coordination problems
- dry mouth
- red eyes
- slower reaction times
- memory loss
These side effects are part of the compound’s psychoactive properties.
Neither compound is fatal.
However, high THC use may be connected to long-term negative psychiatric effects. This is especially true for adolescents who consume large amounts of THC.
The effect on the brain is more profound for teens. Using the compound increases the risk for some psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia.
CBD vs. THC: Drug testing
Cannabinoids like THC and CBD are stored in the body’s fat. They can show up on drug tests for several days or weeks after you use them.
Not every drug test will be able to detect CBD, but CBD-sensitive tests are available. Most standard drug tests will look for chemicals related to THC, so THC or marijuana use might show up on a screening.
Likewise, hemp can produce some THC in addition to CBD, so a test could be positive for THC even if you’ve not used it.
Why do people talk about THC content in CBD oil if THC and CBD are two different compounds?
CBD and THC are two of the most prominent cannabinoids found in the Cannabis plant. Both marijuana and hemp produce CBD and THC.
However, marijuana has a higher concentration of THC. Hemp has a higher concentration of CBD.
The average marijuana strain today contains about 12 percentTrusted Source THC. CBD oil may contain small amounts of THC because it’s present in the hemp plant. CBD can have no more than 0.3 percent THC to be legal at the federal level.
Takeaway
 CBD and THC both have medical benefits. They’re also both considered safe, but consider the possibility of side effects and interactions with other drugs you’re taking. Continue your research and talk with your doctor if you have any questions.
CBD and THC both have medical benefits. They’re also both considered safe, but consider the possibility of side effects and interactions with other drugs you’re taking. Continue your research and talk with your doctor if you have any questions.
| TAKEAWAY | CBD | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | YES | YES |
| Decreases Seizures | YES | NO |
| Eases Depression | YES | NO |
| Eases Migraines | YES | YES |
| Helps with Insomnia | YES | YES |
| Helps with Psychosis | YES | NO |
| Hemp-Derived | YES | NO |
| Illegal | YES* | NO |
| Increases Appetite | No | YES |
| Interact with Endocannabinoid System | YES | YES |
| Marijuana Derived | YES* | YES |
| Pain Reliever | YES | YES |
| Produces a "High" | NO | YES |
| Reduces Anxiety | YES | YES |
| Reduces Nausea | YES | YES |
| Shows on Drug Test | POSSIBLY** | YES |
| Side Effects | ALMOST NONE | PSYCHOACTIVE SIDE EFFECTS |
| Used for Various Conditions | YES | YES |
* CBD can be extracted from hemp (cannabis plants that contain less than 0.3 percent THC) or from marijuana plants (cannabis plants with higher concentrations of THC).
** CBD isn’t detected in hemp products, but hemp products may contain trace amounts of THC. THC may show up in high enough concentrations to produce a positive drug test.
Is CBD Legal?
Marijuana-derived CBD products are illegal on the federal level, but are legal under some state laws. Hemp-derived CBD products (with less than 0.3 percent THC) are legal on the federal level, but are still illegal under some state laws. Check your state’s laws and those of anywhere you travel. Keep in mind that nonprescription CBD products are not FDA-approved, and may be inaccurately labeled.
Let’s Revisit the Medical Benefits of CBD
The list of conditions CBD may help with is ever-expanding. Here are some of the most common conditions and symptoms patients combat with CBD:
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders
- Pain and inflammation
- PTSD and anxiety
- Crohn’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Opioid withdrawal
Though clinical and anecdotal evidence suggests CBD’s benefits in managing different conditions, it became most famous for treating a rare and debilitating form of pediatric epilepsy. Dravet’s Syndrome is notoriously resistant to current approved treatment methods. Sufferers are plagued by seizures, often up to hundreds a day, that worsen as they age and can be life-threatening. Currently, treatment methods include having the child wear an eyepatch, specialized diets, and brain surgery, but all have mixed success rates.
Keep in mind that CBD levels may vary from crop to crop—even from plant to plant. However, below are some strains that have been bred to contain higher CBD levels, so they might be a good place to start. Check the map on their strain page to see if these are sold at a dispensary near you. We also recommend checking with dispensaries about the specifics of their strains’ CBD levels. It’s always a good idea to purchase only lab-tested products that clearly state the CBD/THC levels so you know what kind of experience to expect.
To learn more, read our Blog Post Indica vrs Sativa: Which to Choose?
Click here to Book a Happy Travelers Tour!